Stud bolts
Stud Bolts and nut
Stud bolt Material : Carbon Steel , Stainless Steel
Grades for Stud bolt : B7, B8, B7M, B8M, 8T, 8C
Grades for Nut : 2H, 2HM,8, 8M,8A, 8MA
The quantity of bolts for a flange connection will be given by the number of bolt holes in a flange, diameter and length of bolts is dependent of flange type and Pressure Class of flange.
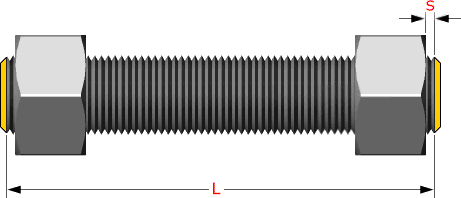
Stud Bolt length are defined in ASME B16.5 standard. The length in inches is equal to the effective thread length measured parallel to the axis, from the first to the first thread without the chamfers (points). First thread is defined as the intersection of the major diameter of the thread with the base of the point.
To download related standards ASME B18.31.2 for stud bolts please click here
To access to standard ASTM A194 please click here
To access to standard ASTM A193 please click here
To access standard ISO 4753 please click here


- Description
- Comments
Stud Bolts general
Stud Bolt length are defined in ASME B16.5 standard. The length in inches is equal to the effective thread length measured parallel to the axis, from the first to the first thread without the chamfers (points). First thread is defined as the intersection of the major diameter of the thread with the base of the point.
the first to the thread without the chamfers (points)
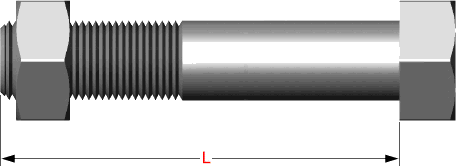
Hex bolts are measured from under the head to the top of de bolt
Note: To allow the use of hydraulic tensioning equipment, larger dimension studs shall be often one diameter longer than "standard". That bolts to have plastic end cap protection.
Threads of Stud Bolts
Bolts threading are defined in ASME B1.1 Unified Inch Screw Threads, (UN and UNR Thread Form). The most common thread is a symmetrical form with a V-profile. The included angle is 60°. This form is widely used in the Unified thread (UN, UNC, UNF, UNRC, UNRF) form as the ISO / metric threads.
The advantage of a symmetrical threads is that they are easier to produce and inspect compared with non-symmetrical threads. These are typically used in general-purpose fasteners.Thread series cover designations of diameter/pitch combinations that are measured by the number of threads per inch (TPI) applied to a single diameter.
Standard Thread Pitches
Coarse thread series (UNC/UNRC) is the most widely used thread system and applied in most of the screws, bolts and nuts. Coarse threads are used for threads in low strength materials such as iron, mild steel, copper and softer alloy, aluminium, etc.. The coarse thread is also more tolerant in adverse conditions and facilitate quick assembly.
Fine thread series (UNF/UNRF) is commonly used in precision applications and in there where require a higher tensile strength than the coarse thread series.
8 - Thread series (8UN) is the specified thread forming method for several ASTM standards including A193 B7, A193 B8/B8M, and A320. This series is mostly used for diameters one inch and above.